Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
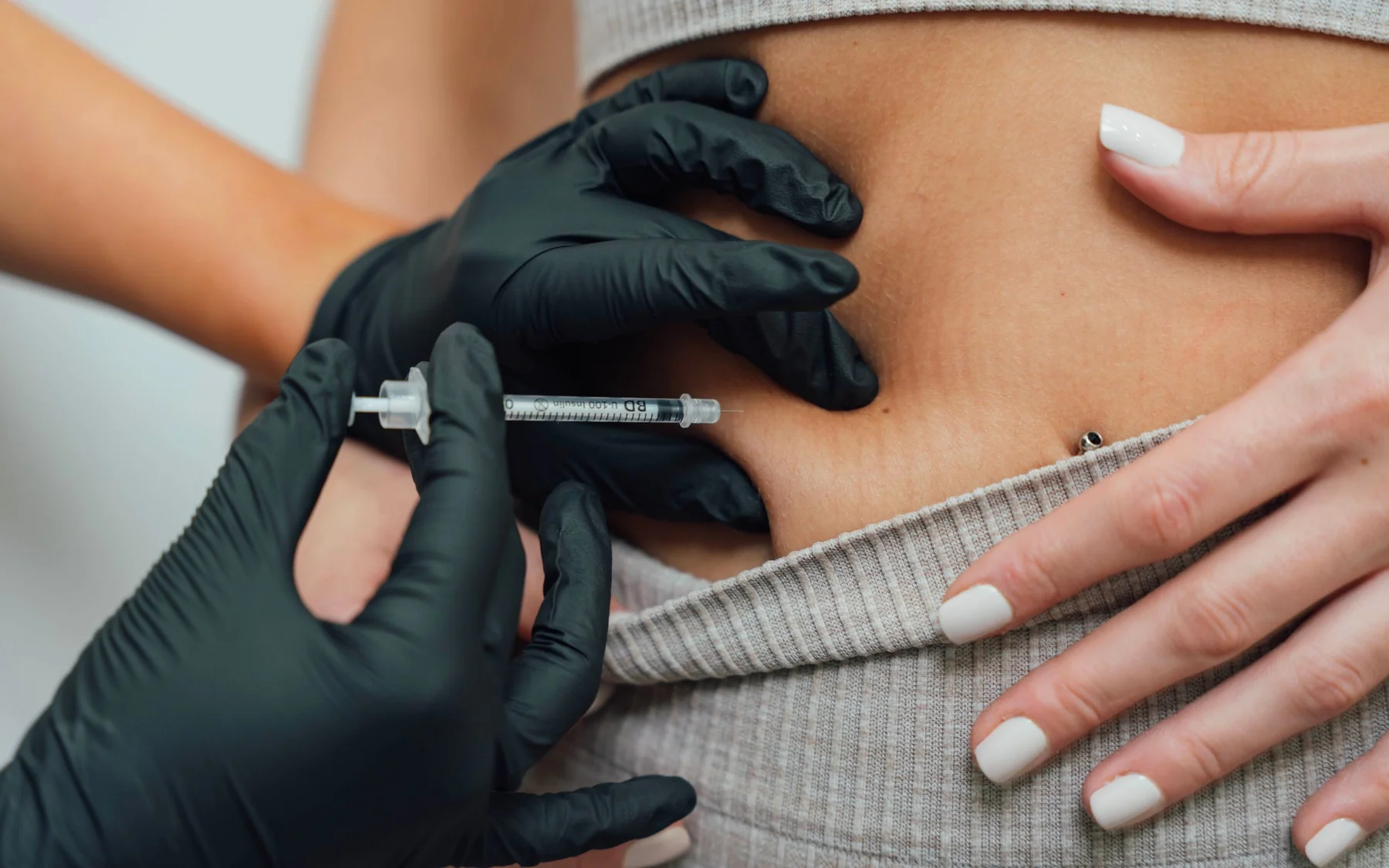
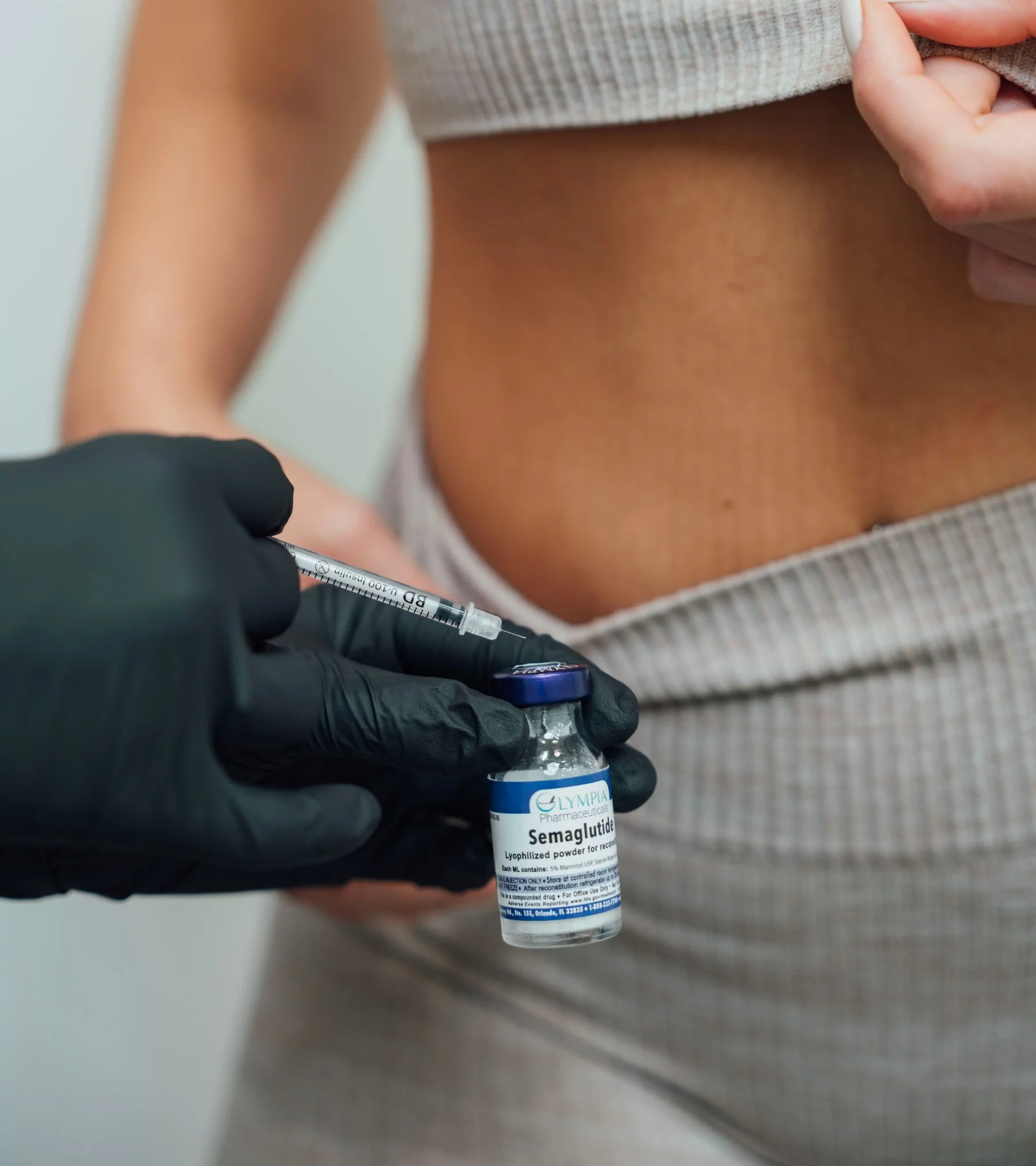
If you have lost weight in the past only to have it return, Semaglutide and Tirzepatide may offer the support you need to lose weight and keep it off. These once-weekly injectable prescription medications are designed to assist with long-term weight management by helping regulate appetite, improve satiety, and support sustainable results.
How does this service help me?
Key questions answered
What is Semaglutide?
What is Tirzepatide?
How do these medications help me lose weight?
Who are Semaglutide and Tirzepatide for?
How are they administered?
Are there any side effects?
How do Semaglutide and Tirzepatide compare?
Still unsure? Take a deep dive into our treatments, services, and products in our articles and write-ups section. Find key info, learn it all.